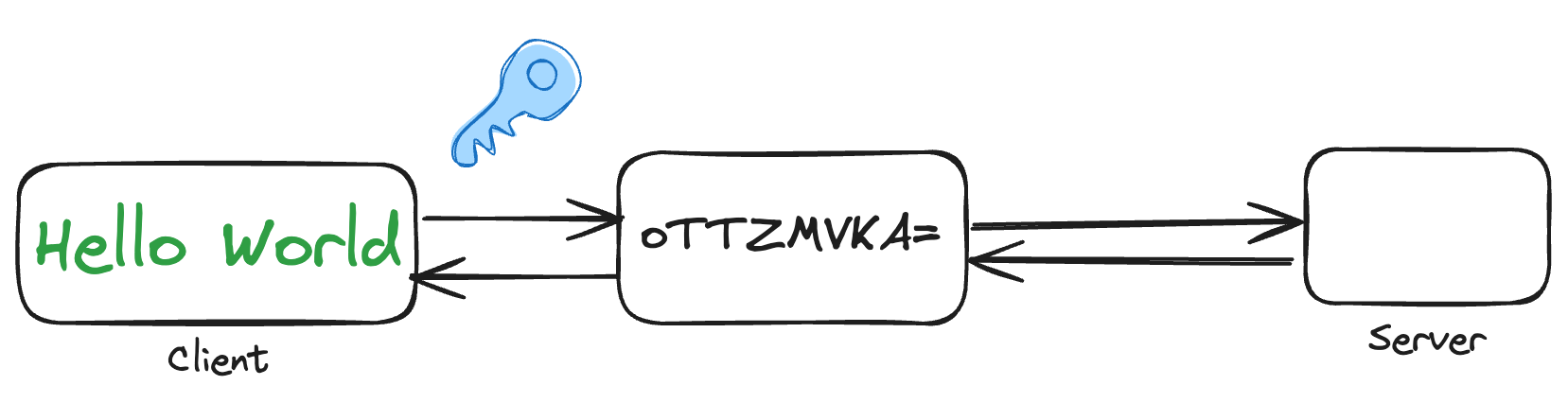
Client-side encryption refers to the practice of encrypting data on the client side (user's device) before it is transmitted to a server or stored in a remote location. This approach enhances the security and privacy of user data by ensuring that sensitive information is encrypted locally, and only the encrypted form is transferred or stored on the server.
Here's how client-side encryption typically works:
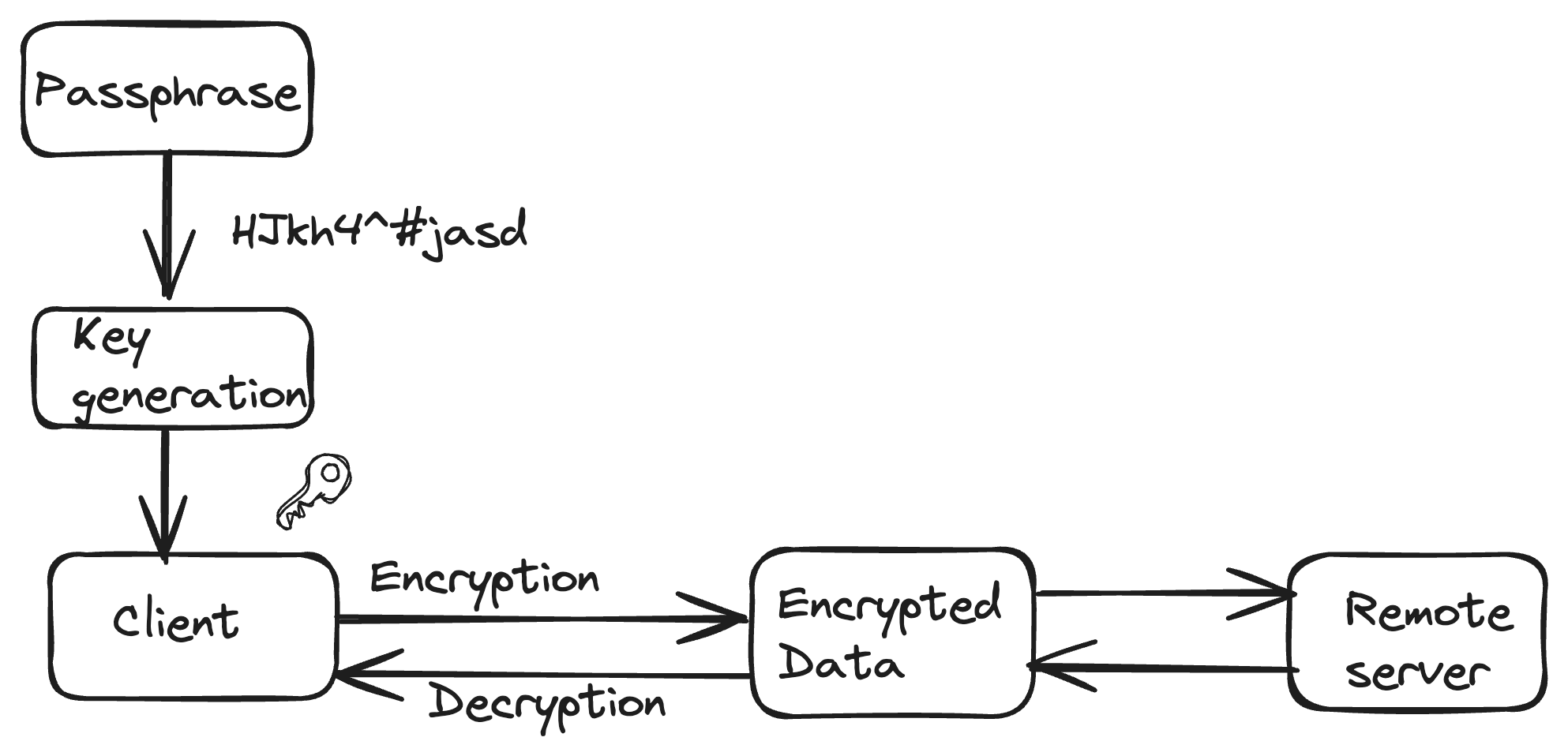
For the first time setup the keys are generated which are typically the master-keys. These keys are used to encrypt and decrypt. They are derived from user entered passphrases.
In cloud services before the client sends the data to the server, the client encrypts the data using the generated encryption key. Most commonly AES encryption is used as the encryption algorithm. Once the data is encrypted, it is transmitted to the remote server and stored in encrypted form, even if the data is intercepted it is in unreadable form without corresponding decryption key.
While reading the data the server transmits the encrypted data back to the client and client decrypts the encrypted data using the encryption key. This step ensures the sensitive information remains secure as decryption occurs on the user's trusted services.
In some cases, client-side encryption is used in conjunction with end-to-end encryption (E2EE), where only the end users (clients) have the keys to decrypt and access the data. This ensures that even service providers or server administrators cannot access the unencrypted data.
Client-side encryption is commonly implemented in various applications and services, such as:
Cloud Storage Services: Users can encrypt their files locally before uploading them to the cloud, ensuring that the cloud service provider cannot access the content.
Messaging Apps: End-to-end encryption in messaging apps ensures that only the intended recipients can decrypt and read the messages.
File Transfer Services: Encrypting files before transferring them over the internet ensures the confidentiality of the data during transit.
This approach empowers users with greater control over their data and adds an extra layer of security, especially in scenarios where users may not fully trust the server or the service provider with their sensitive information.
Benefits of Client-side encryption
Client-side encryption offers several advantages, particularly in enhancing the security and privacy of user data. Here are some key benefits:
Enhanced Data Security:
Client-side encryption ensures that sensitive data is encrypted on the user's device before being transmitted or stored remotely. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches.
User Control: Users have greater control over their encryption keys and, consequently, their data. This empowers individuals to manage and safeguard their information, reducing dependence on service providers.
Privacy Preservation: Client-side encryption enhances user privacy by preventing service providers or third parties from accessing unencrypted user data. Only users with the corresponding encryption keys can decrypt and access their information.
Reduced Trust in Service Providers:
Users don't need to fully trust service providers with their unencrypted data. Even if the service provider is compromised, the encrypted data remains unreadable without the encryption keys.
Compliance with Privacy Regulations: Client-side encryption aids in compliance with data protection and privacy regulations by ensuring that sensitive information is secured at the source, reducing the risk of non-compliance.
Challenges with client-side encryption
Client-side encryption, while offering enhanced security and privacy, comes with its own set of challenges and considerations:
Key Management: Effective key management is critical. Lost or forgotten encryption keys can result in permanent data loss, and securely storing and recovering keys can be challenging.
User Experience: Implementing seamless user experiences, especially around key generation and storage, can be complex. Striking a balance between security and user-friendliness is essential.
Key Distribution: In scenarios where multiple devices or users need access to encrypted data, securely distributing and managing encryption keys becomes a significant challenge.
Recovery Mechanisms: Implementing secure and user-friendly key recovery mechanisms is important. Users should have a way to regain access to their encrypted data if they forget their password or lose their encryption key.
Search and Indexing: Searching and indexing encrypted data becomes challenging, as the server cannot directly access the content. Techniques like searchable encryption may be used, but they add complexity.
Despite these challenges, client-side encryption remains a valuable approach for securing user data, particularly in scenarios where users prioritize privacy and want control over their information. Addressing these challenges requires careful planning, a user-centric approach, and ongoing efforts to stay abreast of advancements in encryption technologies and best practices.
Several well known implementations of client side encryption in cloud services are Amazon S3, AWS Wickr, Azure blob storage, Snowflake, MongoDB.
